Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) play a pivotal role in Mauritania, representing nearly 80% of the country's economic fabric, contributing approximately 30% of the GDP, and generating around 45.8% of the jobs. Despite their importance, access to financing, training programs, and support services remains a significant obstacle to their development.
According to the Global Findex 2018, only 20% of the Mauritanian population over the age of 15 has a financial account, with women being five percentage points less likely than men to have one. Mauritanian SMEs also face a deficit in compliance with standards and certifications, limiting their access to local, African, and international markets. These challenges are also coupled with an increasing frequency and severity of climate disasters, notably droughts, which have risen by 29% over the past two decades, underscoring the urgency to enhance the resilience of SMEs.
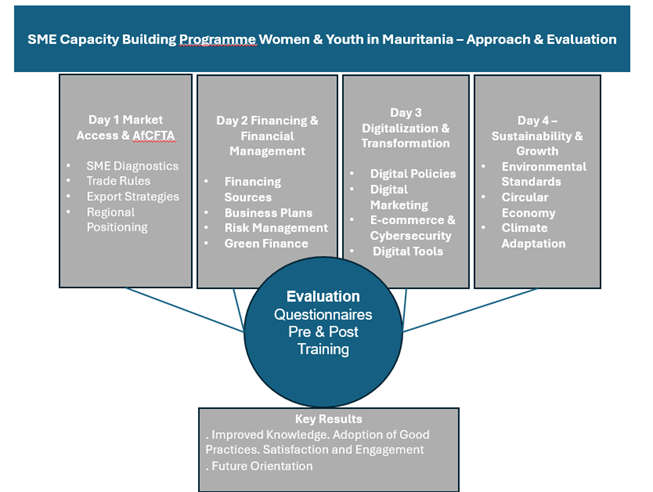
The Sub-Regional Office for North Africa of the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA-SRO-NA) collaborated with Mauritania to develop a tailored SMEs Program that was rolled out to more than 40 SMEs during the period (2024-2025). This program is anchored within the second pillar of the logical framework for employment developed by the Ministry of Youth Empowerment, Employment, Sports, and Civic Service of Mauritania, specifically supporting small and medium-sized enterprises. The first pillar is active employment policies, and the third one is boosting job supply and demand. The program focuses on addressing the challenges of Mauritania’s entrepreneurial ecosystem through an integrated approach that builds on four essential pillars (Figure 1).
The program includes pre- and post-training evaluation questionnaires, two introductory webinars, and in-person sessions that comprise technical presentations, case studies, and practical workshops.
Toward Improved Export, Digital, and Green Skills for Women- and Youth-Led SMEs
In 2023, ECA-SRO-NA launched a capacity-building program for women-led SMEs in Morocco. In 2024, the program expanded to include Mauritania and Libya. In 2025, the SMEs program is being rolled out for Libyan, Mauritanian, and Tunisian SMEs. To date, nearly 430 women and youth SME leaders have enhanced their capabilities in areas such as market access—particularly in Africa—finance, digital tools, and sustainable business practices.
As part of the initiative, two online awareness webinars were held on June 26 and July 3, 2025, to introduce the program’s components to beneficiaries. These sessions enabled female and young SME leaders to enhance their knowledge and awareness of the key identified areas—through interactive discussions with ECA experts.
The workshop, held from July 8 to 12, provided a multi-stakeholder platform connecting youth and women with relevant national stakeholders and inclusion programs, such as the one developed by the Central Bank of Mauritania, the Commerce Chamber, the Ministry of Empowerment of Youth, Employment, Sports, and Civic Service-particularly the Program “VADDAT”. The participants also enhanced their awareness of existing work and opportunities provided by United Nations agencies, including the World Bank, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), through their activities in support of female entrepreneurship and economic empowerment, as well as the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (The E-trade for Women Initiative). International partners also include the World Trade Organization (Global Trade Helpdesk and SMEs support programs), the International Labour Organization (Social finance and financial inclusion initiatives), and the International Trade Centre (E-commerce and digital platforms for export).
Participants were also introduced to the African Trade Portal, including the Africa Trade Platform (ATEX), as part of a partnership with the African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank). This tool represents a strategic lever for strengthening Mauritania's integration into continental trade. According to data from the National Agency for Statistics, Demographic and Economic Analysis, Mauritania currently accounts for 10% of intra-African imports and 13% of exports, highlighting significant potential for development.
As a result of this program, female and youth entrepreneurs developed their capabilities to devise strategies for improving market access, utilizing digital technologies and platforms, designing business and export development plans, and analyzing and mitigating financial and climate risks.
By Adam Elhiraika, Wafa Aidi, and Oumaima Tounchibine

![[Blog] Empowering women- and youth-led SMEs in Mauritania](https://www.uneca.org/sites/default/files/styles/slider_image/public/storyimages/shutterstock_2366901731_1920x640.jpg?itok=wAbUem8T)